How Are Neutral Links and Terminal Blocks Different?
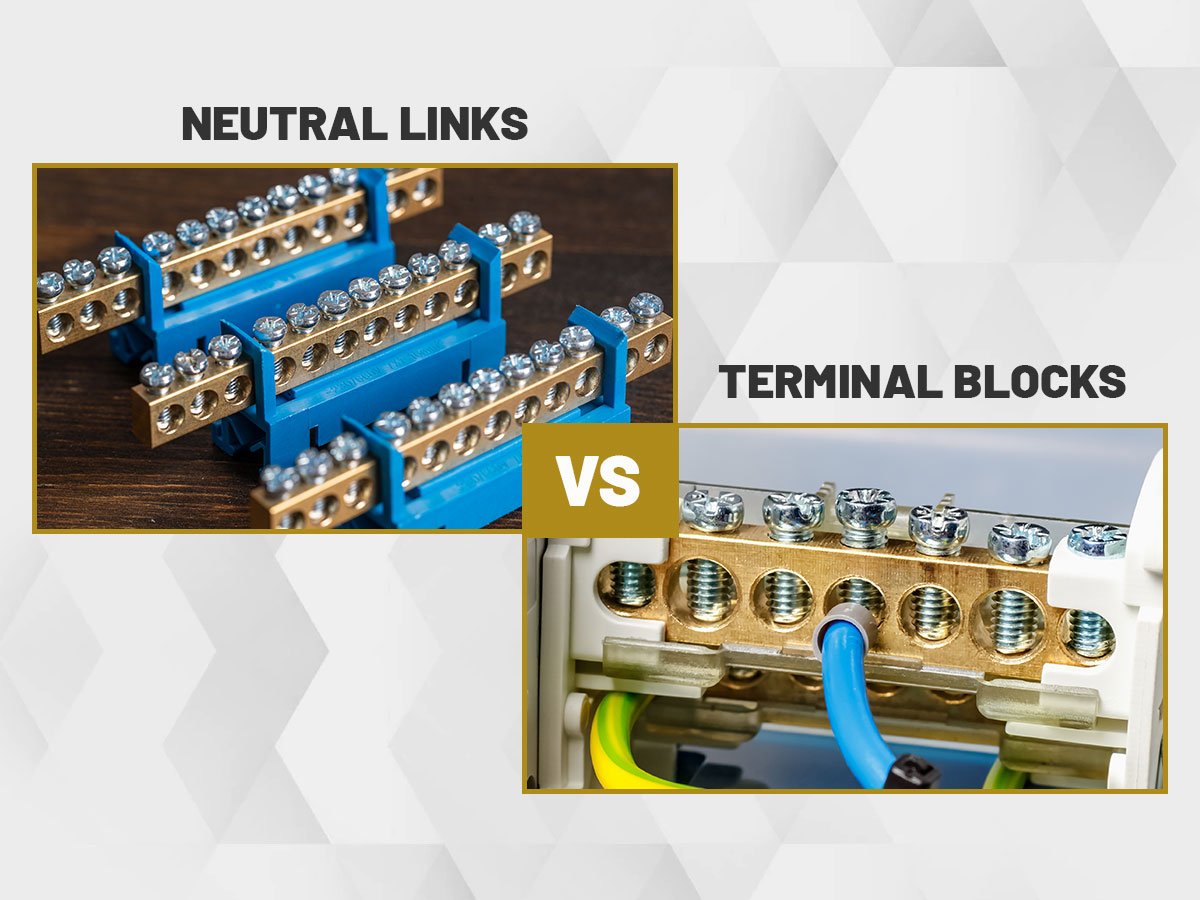
The neutral links and terminal blocks are the most common electrical components which are used in variety of industries like electrical, electronics, telecommunication, and more. It’s a common assumption that neutral links and terminal blocks refer to the same industrial application. But even though they look similar, they are two unique electrical components with their own unique role and applications. As a professional and quality manufacturer of neutral links and terminal blocks, we have encountered many customers who often confused for using both these components for different industrial applications. So, we have obtained some differences and similarities between neutral links and terminal blocks in this article.
The differences between neutral links and terminal blocks:
| Neutral Links | Terminal Block |
| A neutral link is a small piece of metal that acts as a terminal in a circuit. | A terminal block is a modular block that secures two or more wires together. |
| The neutral link is also known as a neutral bar or neutral link connector. | A terminal block is also known as a connection terminal or terminal connector. |
| The majority of neutral links are found in Energy Meters, Electrical Switches, and Smart Electric Meters. | A terminal block connects panel-mounted equipment to the power and field wiring. (such as controllers, PLCs, I/O modules, etc.) |
| A neutral link in an AC circuit serves as a return path for the flow of current. | The terminal block is widely used on panel boards for the mounting of other electrical devices. |
| It provides a returning point to the flow of electricity. | It provides a convenient, economical and safer way to distribute power from a single input source to multiple outputs. |
| In the electrical system, neutral links are the terminating point of neutral wires. | In an electrical system, a terminal block secures two or more wires together and manages complex electrical circuits. |
| A neutral link is used to terminate more than one wire or circuit. | They are used for connecting wires to ground or earth connections. |
| Aluminium neutral links are the most common, although brass neutral links are found in some countries as well. | The majority of terminal blocks are made from copper alloys to ensure very low contact resistance. |
| Neutral links may classify or vary depending on the number of neutral wires that need to be terminated, and the material they are made from. | Terminal blocks can be classified on the basis of structure, device type, termination options etc. |
| A neutral link is a key component of building protection devices such as MCBs, switchgear, circuit breakers, and RCDs. | The terminal block is a crucial electrical component that is used for signal connections or to distribute power within a control panel. |
| A neutral link protects electric circuits from overload damage. | Connections using terminal blocks should adhere to the safety standards of the Electric Supply Industry. |
| A neutral link is crucial for isolating electric equipment and repairing faulty downstream equipment. | Terminal blocks increase safety by grounding, isolating, and protecting the other components in the electrical circuit. |
| The neutral wire can be easily secured using different types of metal screws. | The wires are securely connected to current bars with the help of clamps; these clamps can be screw clamps, spring clamps, nut & bolt or studs. |
| Types of neutral links including industrial neutral links, DIN Rail neutral links, regular duty neutral links, heavy duty neutral links, pluggable neutral links, etc. | Types of terminal blocks including barrier terminal blocks, power distribution terminal blocks, single-stud terminal blocks, panel mounting terminal blocks, modular terminal blocks, etc. |
| Neutral link is usually White or Grey in color code. | There are different colour code such as Green/yellow (green with a yellow stripe) for protective ground, blue for neutral and brown or black (the unmarked grey terminal) for hot. |
The similarities between neutral links and terminal blocks:
- Terminal blocks and neutral links both provide more flexibility.
- Wiring modifications are easy because wires can be removed or added quickly.
- They are essential parts of the functioning of an electric device, it is a safety feature.
- When individuals are grouped or clustered together, they can be used as a multi-level configuration that saves space.
- Both are important components in any industrial setting.
- There are insulated frames available for the neutral link and terminal block that have the sole purpose of securing two or more wires.
- Terminal blocks and neutral links are closely related, but they are not the same.
- Neutral links and terminal blocks both are ideal for various industrial applications such as electrical, telecommunication, heavy machinery manufacturing, electronics, hydraulic, medical, aerospace, Military, building construction, oil & gas, robotics, and many others, because of their mechanical, electrical, and chemical characteristics.
Neutral links vs Terminal block: Which one is best for your application?
Understanding the properties, features, difference, and similarities of neutral links and terminal blocks are crucial to select the right electrical components for your application. It helps to provide answers to the age-old question “Which one is suitable from neutral links and terminal blocks for my industrial application?” The detailed information will make you to differentiate both electrical components (neutral links and terminal blocks) are more valuable for their specific applications.
If you need standard or custom neutral links or terminal blocks, Teron Metal Components is quality manufacturer, and exporter you can trust. No matter whether your requirement is low, medium, or high-volume, or if you are looking for contract manufacturing of neutral links or terminal blocks, request a free quote or get in touch with us via e-mail at sales@teronmetalcomponents.com. We are happy to hear from you!



