Bus Bar vs. Terminal Block: Choose the Right Power Distribution Solution.

The bus bars and terminal blocks are two commonly used electrical components in power distribution systems. They both play a crucial role in routing and distributing power, but they are different in their design, applications, and advantages. If you want to choose the right power distribution solution for your specific electrical wiring needs, you must understand the differences between bus bars and terminal blocks. In this article, we will compare bus bars and terminal blocks, highlighting their key features and applications that help you to make an informed decision for your industrial electrical projects.
Bus Bar: A Backbone for Heavy Power Distribution
Bus bars are solid bars or strips made of conductive materials like copper or aluminium. They serve as a centralized point to collect and distribute high currents across an electrical system. Due to their robust construction, bus bars are ideal for heavy-duty power applications, such as switchgear, distribution boards, and power panels. Based on different purposes, electrical bus bars manufacturers offer various types such as ground bus bars, battery bus bars, marine bus bars, neutral bus bars, terminal bus bars, automotive bus bars, PCB bus bars, power bus bars, vertical bus bars, insulated bus bars, bus bar strip, etc.

Key features of Bus Bars
- High Current Capacity: Bus bars are typically made from highly conductive material such as copper or aluminium, available with low resistance and high current-carrying capacity.
- Low Resistance: The solid design of bus bars results in low electrical resistance, reducing power losses during transmission.
- Low voltage-drop: Due to their low resistance, they minimize voltage drop over long distances, ensuring efficient power transmission.
- Compact Design: They offer a compact solution for power distribution compared to traditional cabling system, saving space, and reducing installation complexity.
- Easy installation: They allow for straightforward installation and interconnection, streaming the wiring process.
- Heat dissipation: The design of busbars allows for effective heat dissipation, preventing overheating during high current loads.
Application of Bus Bars
- Switchgear and substation: They are extensively used in switchgear and substations to interconnect different equipment, such as circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and another protective device. They facilitate the transfer of power between those components and are crucial for the overfall function and safety of the power distribution system.
- Electrical panels and distribution boards: In electrical distribution panels and boards, they are serving as the main conductive backbone for connecting circuit breakers, fuses, and other electrical devices. They ensure that the power is routed effectively to the required circuits.
- Power electronics: Bus bar is the critical part of power electronics system such as inverters and converters, were they interconnect power semiconductor devices (i.e., MOSFETs, IGBTs) to from power circuits. This ensures efficient power conversation and distribution in applications like renewable energy systems and motor drives.
- Grounding and earthing: They are also utilized as grounding conductors in electrical system to provides a low-impedance path for fault current, ensuring the safety of personal and equipment during fault condition.
- Heavy-duty applications: In heavy-duty applications, such as in power transmission and distribution substation, they are used to handle the significant current and voltage levels safety and efficiently.
- High current applications: They are employed in high-current application, such as data centers, industrial machinery, and large motors, where a substantial amount of electrical power needs to be distributed safety and effectively.
- Electric Vehicle (EVs): In electric vehicles, they are used to interconnect battery cells and modules. They provide a low-resistance pathway for the flow of high-current between the battery packs and the vehicle’s power electronics.
- Renewable energy system: They are employed in solar power and wind power installation to carry and distribute generated electricity.
- High-rise buildings: For large-scale power distribution in commercial and residential building, they are used in main distribution panels.
Terminal Block: Versatile and Modular Power Distribution
Terminal blocks are electrical modular connectors that allow for easy and organized termination of multiple electrical wires. They consist of insulated blocks with metal screws to secure the wires. Several terminal block manufacturers offer din rail terminal blocks, battery terminal blocks, fused terminal blocks, ground terminal blocks, PCB terminal blocks, barrier terminal blocks, marine terminal blocks, ceramic terminal blocks, insulated terminal blocks, 12V terminal blocks, and custom terminal blocks to meet individual needs. Terminal blocks are widely used in low to medium current applications and are known for their flexibility and versatility.

Key Features of Terminal Blocks:
- Versatility: They can accommodate a wide range of wire sizes and types, making them suitable for various applications.
- Individual connections: Each wire is independently terminated, providing flexibility in wiring and facilitating more straightforward maintenance.
- Modularity: Terminal blocks are modular components, making adding or removing connections as needed conveniently.
- Number of connections: They come in various sizes and configurations, offering multiple numbers of connection points to accommodate different wiring needs.
- Mounting flexibility: They can be mounted on DIN Rails, PCBs, or directly onto panels, providing flexibility in installation.
- Voltage rating: They are rated for specific voltage levels to ensure they can handle the electrical load without risk of damage or failure.
Application of Terminal Blocks:
- Power distribution panels: They are frequently used in power distribution panels to connect and distribute electrical power from a main power source to various circuits, devices, or systems. They allow for easy and organized connections of multiple conductors.
- Industrial control panels: They are extensively used in industrial control panels to connect control signals, sensors, actuators, and other devices. They simplify wiring and facilitate the troubleshooting and maintenance of the control system.
- Building wiring and electrical cabinets: They are employed in building wiring systems and electrical cabinets to connect electrical devices such as switches, outlets, and lighting fixtures.
- Motor Control Centres (MCCs): In MCCs, they are used to connect and control electric motors. They provide a convenient way to connect motor leads and control circuits.
- Process Automation: They are used in process automation and instrumentation systems to connect sensors, transmitters, and other control elements to control panes or distribution control systems.
- Railways and transportation: They are used in the railway system for various electrical connections, such as signalling, lighting, and communication systems.
- HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning): They are found in HVAC systems for connecting electrical components like motors, fans, and sensors.
- Power supplies: In power supply units and UPS (uninterruptible power supply) systems, terminal blocks are used to connect input and output wires to the power source and the load.
- Renewable energy systems: They are used in solar power systems and wind turbines to connect solar panels, wind generator outputs, and battery banks.
- Audio and video equipment: In audio and video systems, they are used for connecting speakers, amplifiers, and other audio/video components.
- Test and measurement equipment: Electrical metal terminal blocks are used in test and measurement equipment to facilitate easy connections for measuring electrical signals.
- Automotive applications: They are utilized in automotive wiring harnesses for various electrical connections within the vehicle.
How are terminal blocks and bus bars different?
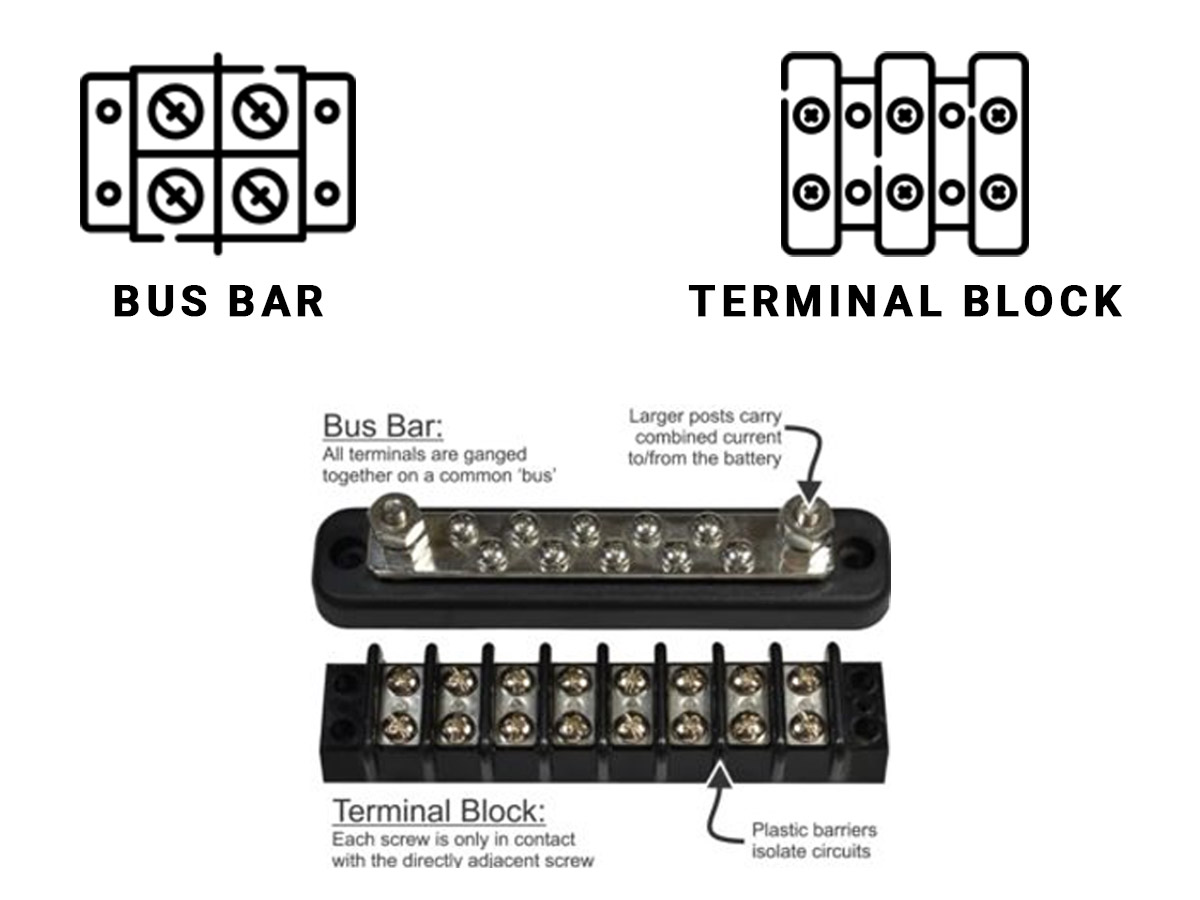
The terminal block has separated circuits where each incoming wire is paired with an outgoing wire whereas a busbar gathers multiple wires together for power distribution. The easiest way to tell them apart is by the tinned copper body. If the body is one solid piece of metal, then the electricity will be distributed evenly, and as such, is a bus bar. On the other hand, if the body is segmented into pieces of tinned copper separated by plastic ridges, then they are individual circuits, and as such, a terminal block.
Conclusion:
Both bus bars and terminal blocks play critical roles in power distribution, but their distinct features cater to different electrical needs. By understanding the strengths of each solution, you can make an informed decision and ensure an efficient and reliable power distribution system for your project.
Considering all the factors discussed above will help you make the right decision for a power distribution solution. And still, if you are not sure how to choose the right power distribution component, or just want to talk about your custom requirement, then our team of experts at Teron Metal Components can simplify the manufacturing process for you, helping you understand what features and application differentiate them so that you can select the right electrical power distribution component. To learn more about our services and offered range of metal components, contact us at sales@teronmetalcomponents.com or request a quick quote!



